
The typical size ranges are from 30 up to 150 mm diameter in a variety of widths from 50 mm to about 1 meter.
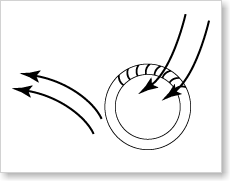
Air is sucked along the small vane in the housing, through the interior of the wheel and back along ejected. In this case, a partial vacuum is created which sucks in air continued.
Moreover, air turbulence created in the interior, supporting the stable flow of the fan.
Another but much smaller proportion of air is carried to the outside wheel.
increase in pressure and flow
Cross flow fan normally produce lower pressure compared to similarly built fans with forward curved impellers, but they reach a higher flow rate.
 This is due to the property of the wide vane.
The volume of each blade is substantially smaller than forward curved fan.
This is due to the property of the wide vane.
The volume of each blade is substantially smaller than forward curved fan.
 The efficiency is relatively low, because the air must pass through the two blades, then suddenly changes direction and also subsequent turbulences occur.
The maximum overall mechanical efficiency is about 40%.
The efficiency is relatively low, because the air must pass through the two blades, then suddenly changes direction and also subsequent turbulences occur.
The maximum overall mechanical efficiency is about 40%.
use
For applications that require large volumes of air at low pressure structure.




