Comfort - a generic term - refers to the condition in which a person is . Personal factors, such as health, psychological, sociological and situational factors are also included.
In the heating, ventilating and air conditioning systems, there is comfort in the condition of the air in which the person feels most comfortable. This air condition also is experienced subjectively.
Thermal comfort and indoor air quality are sub-items of the term comfort.
In the heating, ventilating and air conditioning systems, there is comfort in the condition of the air in which the person feels most comfortable. This air condition also is experienced subjectively.
Thermal comfort and indoor air quality are sub-items of the term comfort.
For details on the thermal comfort of humans is explained in Module I of the Basic Course heating.


Thermal comfort is achieved when
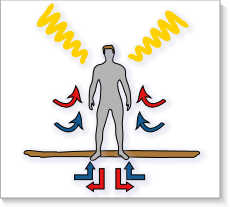
 the constant internal body temperature can be maintained at 37 ° C in humans and
the constant internal body temperature can be maintained at 37 ° C in humans and
 the heat generated can be derived and thus the human body, there is a thermal equilibrium with the environment.
the heat generated can be derived and thus the human body, there is a thermal equilibrium with the environment.
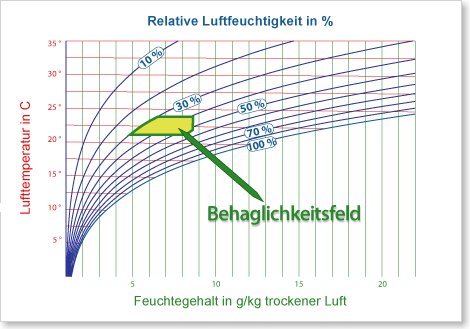
Based on humidity and temperature, there is a so-called comfort zone, in which a person feels comfortable. Outside this field, the man felt discomfort.

Thermal comfort is also determined by these factors:
 Air temperature,
Air temperature,
 Room surface temperatures,
Room surface temperatures,
 Air movement or air velocity,
Air movement or air velocity,
 relative humidity,
relative humidity,
 activities,
activities,
 insulating clothing.
insulating clothing.
Maintaining thermal comfort for occupants of buildings is one of the very important goals of the heating, ventilation and air-conditioning engineer.




